Change in chip thickness for doubled feed but constant chip thickness ratio
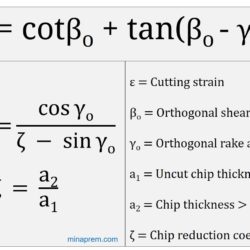
Question: In an orthogonal cutting, the depth of cut is halved and the feed rate is made double. If the chip thickness ratio is unaffected with the changed cutting conditions, what will be the change in actual chip thickness? [IAS 1995] Solution: Chip thickness ratio, also called cutting ratio (rcu), is one important parameter for machining analysis as it indicates the deformation (elongation) of chip in its thickness. Machining is