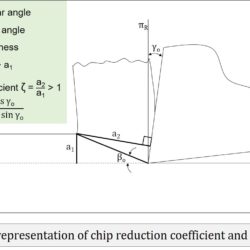
Calculate coefficient of friction from cutting and thrust force for zero rake
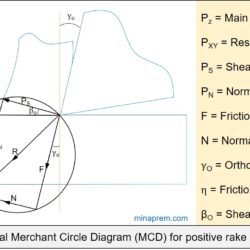
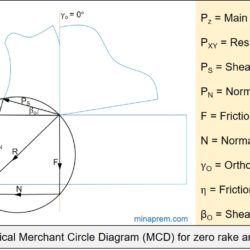
Question: In an orthogonal cutting process the tool used has rake angle of zero degree. The measured cutting force and thrust force are 500 N and 250 N, respectively. What is the coefficient of friction between the tool and the chip? [GATE 2016] Solution: This problem can be solved with the help of Merchant Circle Diagram (MCD). MCD is the graphical representation of various forces associated with an orthogonal machining