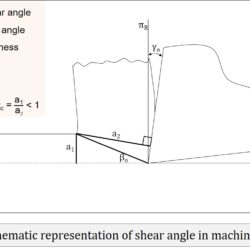
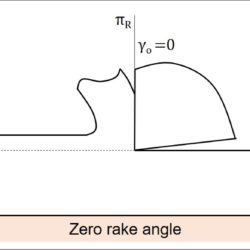
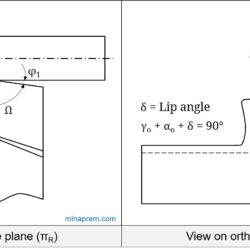
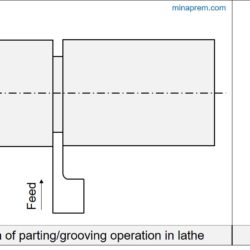
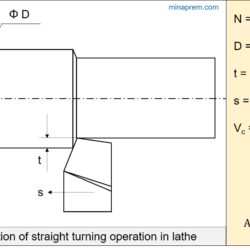
Determine shear angle from orthogonal rake angle and chip thickness ratio
Question: During orthogonal machining of mild steel with a 10° orthogonal rake angle tool, the chip thickness ratio was found to be 0.4. Determine the shear angle. [GATE 2001] Solution: In conventional metal cutting processes, chip gets thickened after machining, and thus chip thickness (a2) becomes larger than uncut chip thickness (a1). The ratio between uncut chip thickness and chip thickness is termed as Chip Thickness Ratio (CTR). Its value