In abrasive jet machining (AJM), work material is removed mainly by erosion and sometime assisted by brittle fracture caused by the impact of fine abrasive grits (size between 10 – 50µm). Type of abrasive as well as its shape, size and other properties influences abrasive jet machining capability. Desired properties of abrasives as well as various abrasives that are commonly used in AJM along with a comparison are discussed in the following sections.
Desired properties of abrasives for AJM
- Abrasive grits must have sharp edges for easy micro-cutting action.
- Abrasive grits should have irregular shape but variation of size within the overall mass should be low.
- Abrasive grits must not contain metal particles as it can cause blockage in pipeline.
- It must have good flow characteristics for smooth flow through pipelines when mixed with carrier gas.
- It should have high hardness and should be rigid enough so that it does not crumbled into parts when striking the work surface.
- Abrasives must not be wet.
- It should be cheap and readily available.
Various abrasives used in AJM
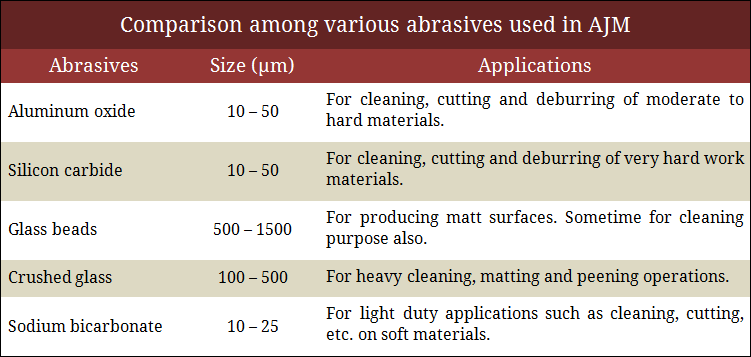
Abrasives are usually selected on the basis of application while average grit size is selected based on the surface finish requirement. Although aluminum oxide (alumina—Al2O3) and silicon carbide (SiC) are two frequently used abrasives, there exist quite a few other abrasives that are used for various purposes to obtain better result. A list of abrasives and their application area are enlisted below. A comparison among these abrasives is also depicted above.
- Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)—Alumina is used for cleaning, cutting and deburring purposes for moderate to hard materials. It has excellent size and shape retention capability.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC)—It is harder abrasive compared to alumina. Thus can be used for all the above purposed but for very hard work materials. Silicon carbide can substantially reduce the nozzle life.
- Glass beads—This is mainly used for producing matt surfaces for reducing transparency.
- Crushed glass—For heavy cleaning, matting and peening operations.
- Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)—Baking soda is commonly used for light duty applications such as cleaning, cutting, etc. on soft materials.
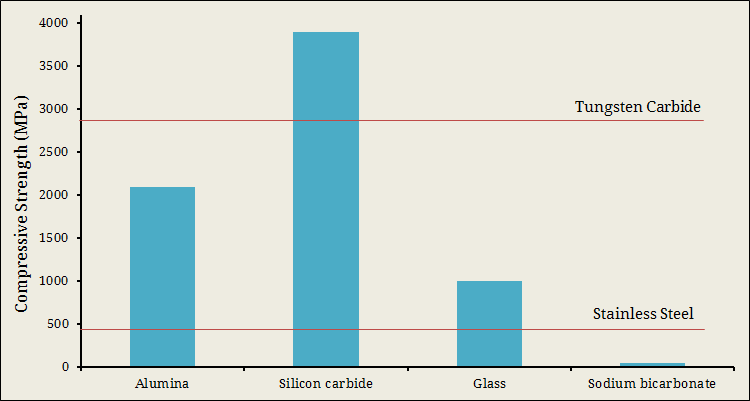
Size of abrasives suitable for AJM
Along with type, abrasive size also influences cutting performance. Smaller size grits can produce highly finished surface but degrade material removal rate (MRR) and thus productivity hampers. Larger grits can again create trouble while mixing and flowing through the pipeline. Higher mixing ratio may cog the nozzle, especially when abrasives contain substantial moisture. Average grain size of abrasives varies from 10 – 50µm. Smaller grain size is used for getting high finish as well as for low duty operations (such as surface cleaning). Larger grains are used for heavy duty applications usually with harder materials.
References
- Book: Nontraditional Manufacturing Processes by G. F. Benedict (Taylor & Francis).
- Book: Unconventional Machining Processes by T. Jagadeesha (I. K. International Publishing House Pvt. Ltd.).